Suppose you are in a hurry and in the Dictionary, you are looking for the page where the words starting with ‘ P ‘ are found. You know that all of the words in the Dictionary are written in alphabetical order. So instead of traversing through all of the pages, you start from any of the middle page and compare the first words initial character with character ‘ P ‘. Lets say the word you found was ‘ Island ‘. Since the word ‘ Island ‘ initial character is ‘ I ‘ and ‘ I ‘ is before ‘ P ‘ in the alphabet, you will again look for the middle page within the page you just found and the last page of the dictionary. You will keep repeating the process until you find the page where the words whose initial character is ‘ P ‘ starts. That’s how Binary Search works.
Now you might be wondering why Binary Search is called ” Binary Search “. There is no 0 and 1 so why ? It is called Binary search because when you divide the dictionary into two you get yourself the left part or right part or should i say 0 and 1. Since you always get 2 parts while dividing and choose one of the part based on your comparison that’s why it is called Binary search.
Now what is this Binary Search Algorithm?
Binary Search is a searching algorithm that is used on a sorted array to find a specific value by dividing the search interval in half multiple time
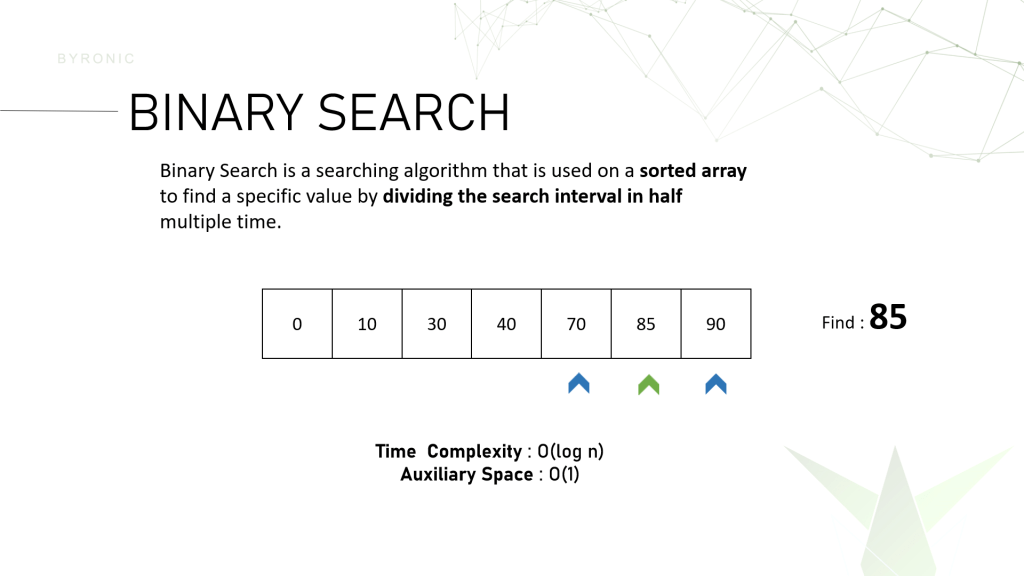
For example, this is a sorted array consisting of 7 numbers and This algorithms job is to find the number 85. So first we will find the middle index and compare that index value with 85. If it doesn’t match then we divide the array and pick a side based on the comparison and keep repeating the process untill the middle index value is equal to the value we are looking for.
The average time complexity of this algorithm is Big O (log n) and the Auxiliary Space is Big O (1)
Now let me show you what is the full process of doing the binary search.
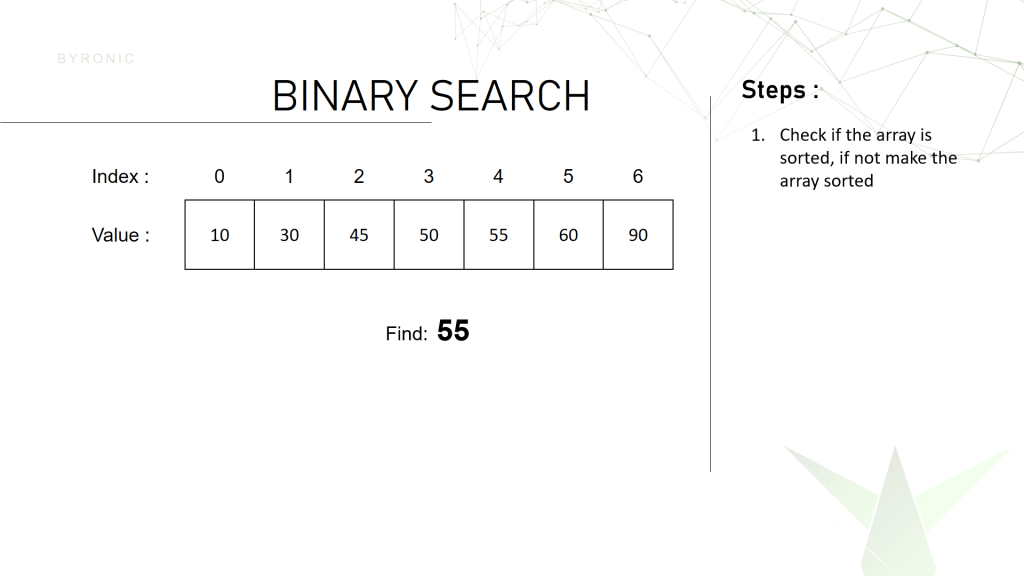
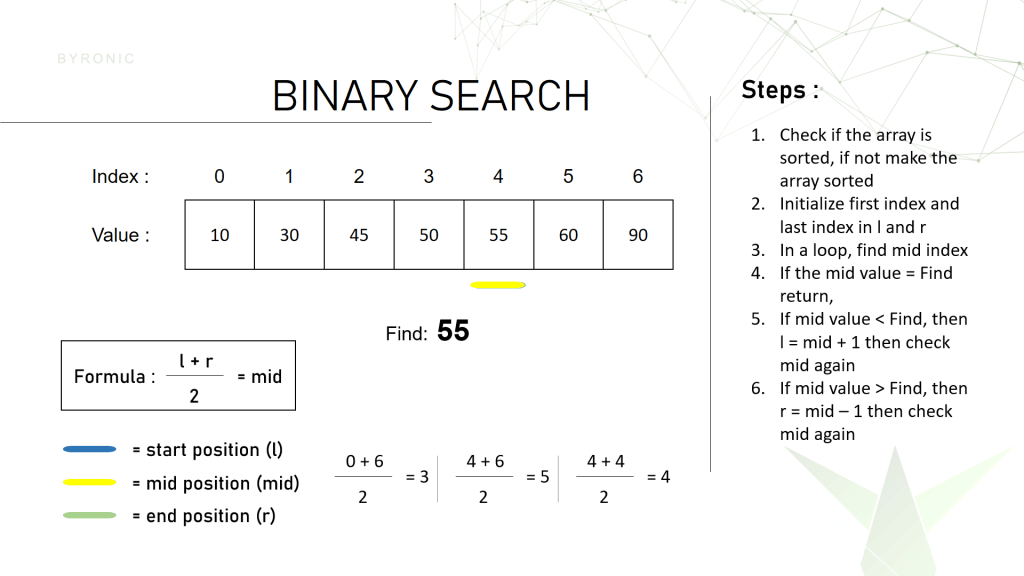
Let’s say we have this array of length 7 and index position starts from 0 to length-1 which is equal to 6. Here we have to find the number 55.
First we have to check if the array is sorted. Remember that this algorithm only works on sorted array. If they array is not sorted then we have to make the array sorted first.
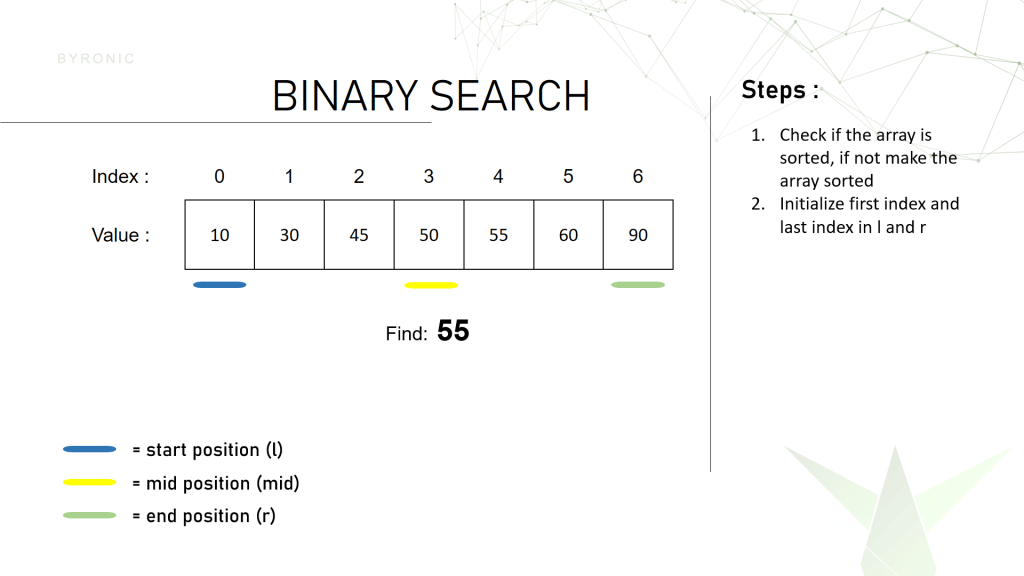
After that we create a variable l and r and initialize them at first with the first index and the last index of the array which is 0 and 6 while in a loop. It will keep changing the value until we find the number.
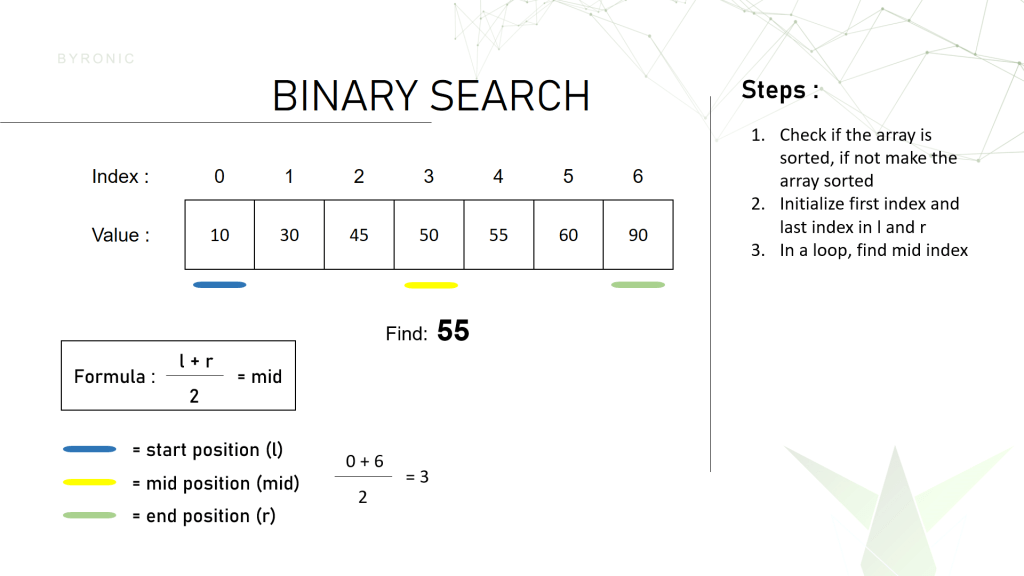
Now using the formula we get that the middle value is 3. Here we compare if the middle index value 50 is equal to 55. For our case it didn’t match with the value. Since 50 < 55, we made our searching area from index 0 to 4 , using l = mid + 1 and again repeat step 2. Why l= mid + 1 ? Because before index 4 there is no way 55 will exist since the array is sorted in ascending order. Now l is equal 4 and r is equal to 6 and the middle value is 5. In index 5 the value is 60 which is greater than the value we are looking for. Since 60 > 55 we have to change the searching area from 6 to 4 using r = mid – 1 because beyond the index 5 the numbers will always be larger than 90. Then we again repeat the process. Now the l = 4 and r = 4 , so middle value is also equal to 4. Since at index 4 the number is equal to 55 so we can say that the number has been found in the array. If we still haven’t found the number we would have returned a value -1 which means not found.
The advantages and disadvantages of this algorithm is-

So we learned a lot. Let’s do a quick summary-

You can find the code for this algorithm in this link :
